Research Projects
We study molecular mechanisms of bioenergetics, inflammation, fibrogenesis, and lipid/cholesterol metabolism in the pathogenesis of obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and alcoholic hepatitis. Our specific research interest is to define how macrophages play crucial roles in disease development and how food components/natural products impact inflammatory signaling and energy phenotypes of macrophages by regulating histone deacetylases using nutrigenomics and cell biology tools.

Epigenetic Regulators of Research Interest
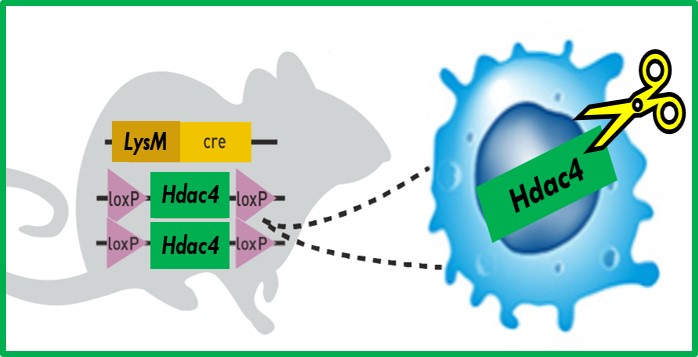
Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4)
Epigenetic regulation via histone modifications, acetylation, in particular, is critical for modulating gene expression. We are interested in the role of HDAC4 in various biological pathways, namely inflammation, fibrogenesis, and lipid and energy metabolism, in the context of obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and alcoholic hepatitis. We are currently studying the functions of hepatocyte and macrophage HDAC4 in mice with cell-specific deletion of HDAC4 in hepatocytes or macrophages generated using the Cre-lox system.

Histone deacetylase 9 (HDAC9)
We study the role of HDAC9 in the regulation of inflammation and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease using global HDAC9 knockout mice. We are also generating Hdac9 floxed mice, which will be used to generate cell-specific roles of Hdac9 using the Cre-lox system, with a primary emphasis on hepatocytes, macrophages, and adipocytes.
Dietary Bioactives and Natural Products of Research Interest

Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is a xanthophyll carotenoid and a red pigment abundant in salmon, shrimp, and lobster. We have studies the health benefits of astaxanthin for more than 10 years. So far, we have shown that astaxanthin exerts potent anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrogenic actions, which help prevent the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mouse models of diet-induced obesity and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
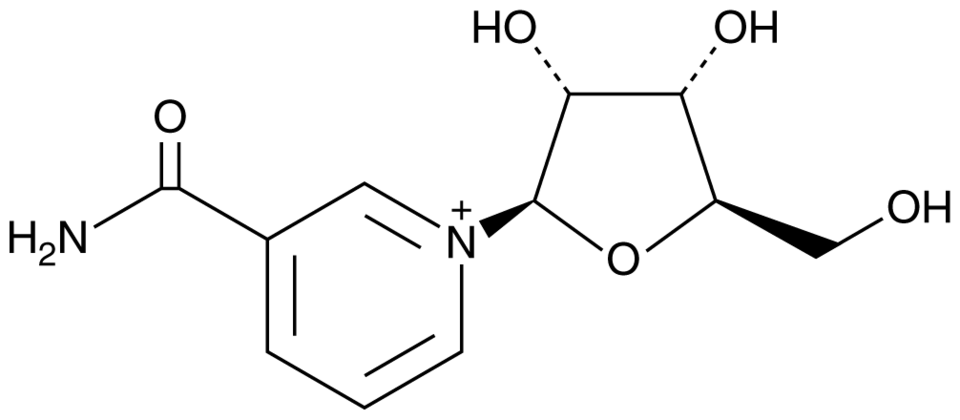
Nicotinamide Riboside
Nicotinamide riboside is an NAD+ precursor. NAD+ is required to activate sirtuins that are crucial for the prevention of obesity, alcohol, and their related metabolic/inflammatory diseases. We are investigating the role of nicotinamide riboside in preventing obesity, non-alcoholic fatty disease, and alcoholic hepatitis.
Blackcurrant
Blackcurrant is a type of berries whose health benefits are under-recognized in the U.S. We have studied the preventive effects of blackcurrant on the development of obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with primarily focusing on inflammation and macrophage phenotypic switch.
Fucoxanthin & Sugar Kelp
Fucoxanthin is another xanthophyll carotenoid abundant in brown seaweed. We study whether fucoxanthin and Connecticut-grown sugar kelp can regulate lipid metabolism, inflammation, and fibrogenesis to prevent obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.

Spirulina platensis
Spirulina platensis is the most-commonly consumed blue-green alga by humans. We have shown that Spirulina has strong anti-inflammatory properties, inhibiting atherosclerosis development in a mouse model of atherosclerosis.
Our research projects have been supported by industry, foundations, and federal agencies.



